Atlantis
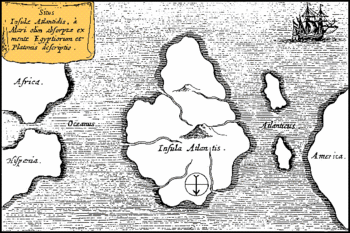
Atlantis (Ancient Greek: Ἀτλαντὶς νῆσος, "island of Atlas") is a legendary island first mentioned in Plato's dialogues Timaeus and Critias, written in c. 360 BC. According to Plato, Atlantis was a naval power lying "across the Pillars of Hercules" that conquered many parts of Western Europe and Africa 9,000 years before the time of the legendary Athenian lawgiver Solon, i.e. in the 10th millennium BC. After a failed attempt to invade Athens, Atlantis sank into the ocean "in a single day and night of misfortune."
The possible existence of Atlantis was discussed throughout classical antiquity, but it was usually rejected and occasionally parodied by later authors. Alan Cameron wrote: "It is only in modern times that people have taken the Atlantis story seriously; no one did so in antiquity".[1] The Timaeus remained known in a Latin rendition by Calcidius through the Middle Ages, and the allegorical aspect of Atlantis was taken up by Humanists in utopian works of several Renaissance writers, such as Bacon's New Atlantis and More's Utopia. In the United States, Donnelly's 1882 publication Atlantis: the Antediluvian World unleashed widespread interests f